GPoS
What is GPoS
There are multiple participants in Crust Network, they are: validator, guarantor, and storage user.
Crust network uses the GPoS (Guaranteed Proof of Stake) consensus, which is a PoS based consensus with storage resources as a guarantee. Similar to existing PoS projects, nodes in Crust Network need to stake CRUs to compete to become validators. The difference is that nodes also need to provide storage resources to obtain the corresponding stake limit. When the node obtains the stake limit, it can obtain the corresponding number of CRU staking.
Through the MPoW mechanism - the node storage status monitoring mechanism, the chain can obtain the node storage capacity through the work report signed by the node's TEE module. The more storage resources a node contributes, the higher the stake limit it can obtain.
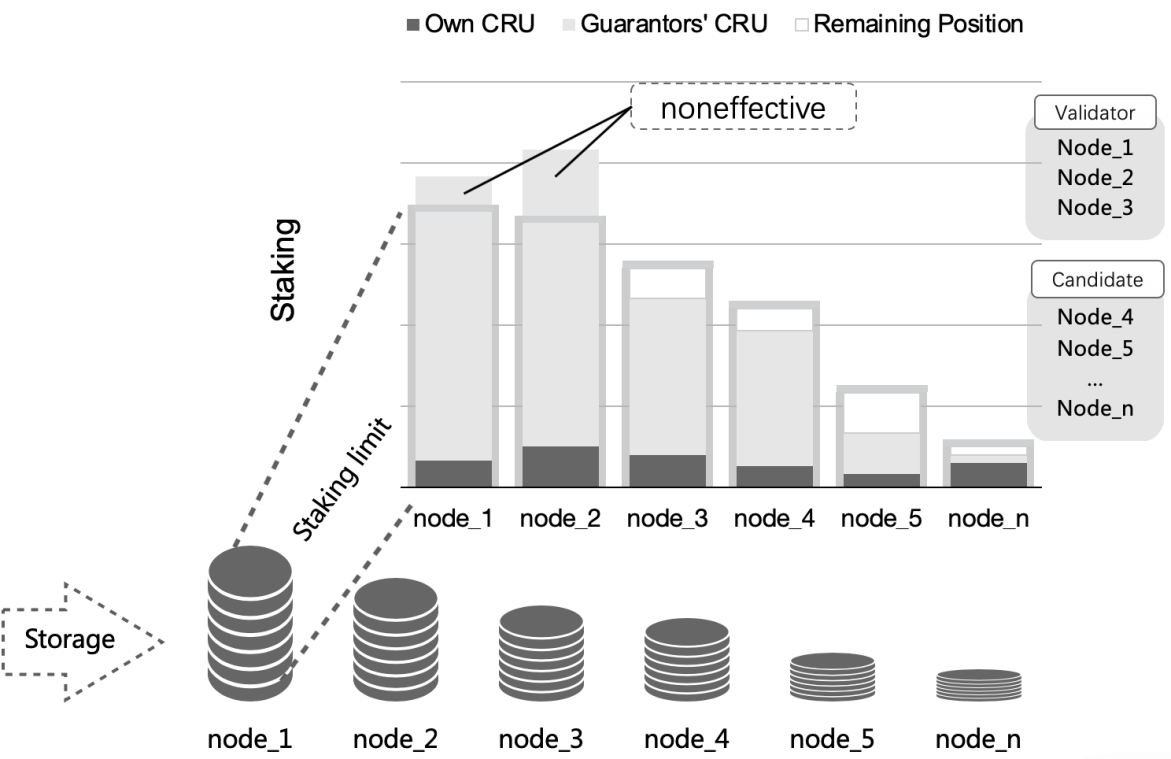
GPoS is based on Substrate framework, the block generation algorithm is BABE/GRANDPA. If someone wants to control this network, in addition to having a large proportion of CRU tokens, they also need to control enough storage resources. Such a design will make the attack more difficult.
Detailed explanation of some terms
- Stake limit: It determines the upper limit of the staking amount that can be calculated during validator election and stake reward calculation. The staking amount exceeding this upper limit will not be included in the calculation process. Its update frequency is one workload reporting period, and the update frequency on the main network is 1 hour.
- Total staking amount: the sum of its own binding amount and the total amount guaranteed by the guarantor. Its update frequency is displayed in real time. When it increases or decreases the bound amount or the guarantor increases or decreases the amount of guarantee, it will be updated in time after refreshing the page.
- Effective stake: The stake limit and the smaller value of the total staking amount. Its update frequency is one era, and the update frequency on the mainnet is 6 hours.
Stake limit calculation
1TB SRD(check the meaning of SRD from glossary) file corresponds to the stake limit of 1CRU, and meaningful files are 1-10 times the stake limit of SRD, please refer to Economic White Paper for the detailed mechanism. Here is only an explanation of the calculation process of the stake limit for meaningful files, and all the contents of the economic white paper are the final criteria.
- Storage power delay: The calculation of the stake limit corresponding to the file has a delay, and the mainnet startup phase is set to 3 months. In the phase of the storage power delay, the stake limit of meaningful files is equal to the stake limit brought by SRD files.
- File storage power: The same file will be stored by different nodes in the Crust network. When the number of nodes stored is larger, the storage power generated by the file will be larger, which can bring up to ten times the stake limit of the file size.
- Deduplication of file storage power: In the same MPoW group, only one member can access the file and obtain the file storage power. Subsequent members receiving the file will be deemed invalid and lose the original SRD file storage power.
How to Join GPoS
Users can join in as validator or as guarantors.
Join GPoS as a validator
To be a validator, please refer to Validator Guide.
Join GPoS as Guarantor
To be a guarantor, please refer to Guarantor Guide.
